Lab 4-4: Mann-Kendall Trend Test#
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy.stats as st
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Load data.
snow_pillows = pd.read_csv('../data/pillows_example.csv')
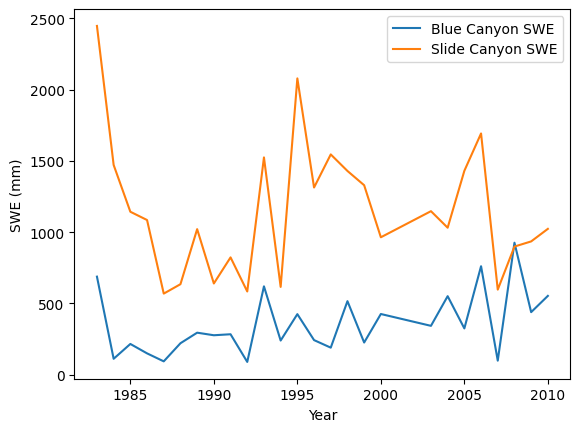
Plot the data
f, ax = plt.subplots()
snow_pillows.plot(x='years', y='BLC_max', linestyle='-', label='Blue Canyon SWE', ax=ax)
snow_pillows.plot(x='years', y='SLI_max', linestyle='-', label='Slide Canyon SWE', ax=ax)
plt.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Year')
ax.set_ylabel('SWE (mm)');
Mann Kendall Test#
def mann_kendall(V, alpha=0.05):
'''Mann Kendall Test (adapted from original Matlab function)
Performs original Mann-Kendall test of the null hypothesis of trend absence in the vector V, against the alternative of trend.
The result of the test is returned in reject_null:
reject_null = True indicates a rejection of the null hypothesis at the alpha significance level.
reject_null = False indicates a failure to reject the null hypothesis at the alpha significance level.
INPUTS:
V = time series [vector]
alpha = significance level of the test [scalar] (i.e. for 95% confidence, alpha=0.05)
OUTPUTS:
reject_null = True/False (True: reject the null hypothesis) (False: insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis)
p_value = p-value of the test
From Original Matlab Help Documentation:
The significance level of a test is a threshold of probability a agreed to before the test is conducted.
A typical value of alpha is 0.05. If the p-value of a test is less than alpha,
the test rejects the null hypothesis. If the p-value is greater than alpha, there is insufficient evidence
to reject the null hypothesis.
The p-value of a test is the probability, under the null hypothesis, of obtaining a value
of the test statistic as extreme or more extreme than the value computed from
the sample.
References
Mann, H. B. (1945), Nonparametric tests against trend, Econometrica, 13, 245-259.
Kendall, M. G. (1975), Rank Correlation Methods, Griffin, London.
Original written by Simone Fatichi - simonef@dicea.unifi.it
Copyright 2009
Date: 2009/10/03
modified: E.I. (1/12/2012)
modified and converted to python: Steven Pestana - spestana@uw.edu (10/17/2019)
'''
V = np.reshape(V, (len(V), 1))
alpha = alpha/2
n = len(V)
S = 0
for i in range(0, n-1):
for j in range(i+1, n):
if V[j]>V[i]:
S = S+1
if V[j]<V[i]:
S = S-1
VarS = (n*(n-1)*(2*n+5))/18
StdS = np.sqrt(VarS)
# Ties are not considered
# Kendall tau correction coefficient
Kendall_Tau = S/(n*(n-1)/2)
if S>=0:
if S==0:
Z = 0
else:
Z = ((S-1)/StdS)
else:
Z = (S+1)/StdS
Zalpha = st.norm.ppf(1-alpha,0,1)
p_value = 2*(1-st.norm.cdf(abs(Z), 0, 1)) #Two-tailed test p-value
reject_null = abs(Z) > Zalpha # reject null hypothesis only if abs(Z) > Zalpha
return reject_null, p_value
Run the Man Kendall tests#
alpha = 0.05
reject_null, p_value = mann_kendall(snow_pillows['SLI_max'].values, alpha)
print('Can we reject the null hypothesis for Slide Canyon?\n{}\n'.format(reject_null))
reject_null, p_value = mann_kendall(snow_pillows['BLC_max'].values, alpha)
print('Can we reject the null hypothesis for Blue Canyon?\n{}\n'.format(reject_null))
Can we reject the null hypothesis for Slide Canyon?
False
Can we reject the null hypothesis for Blue Canyon?
True
